Pityriasis Alba: A Common Skin Disease In Children
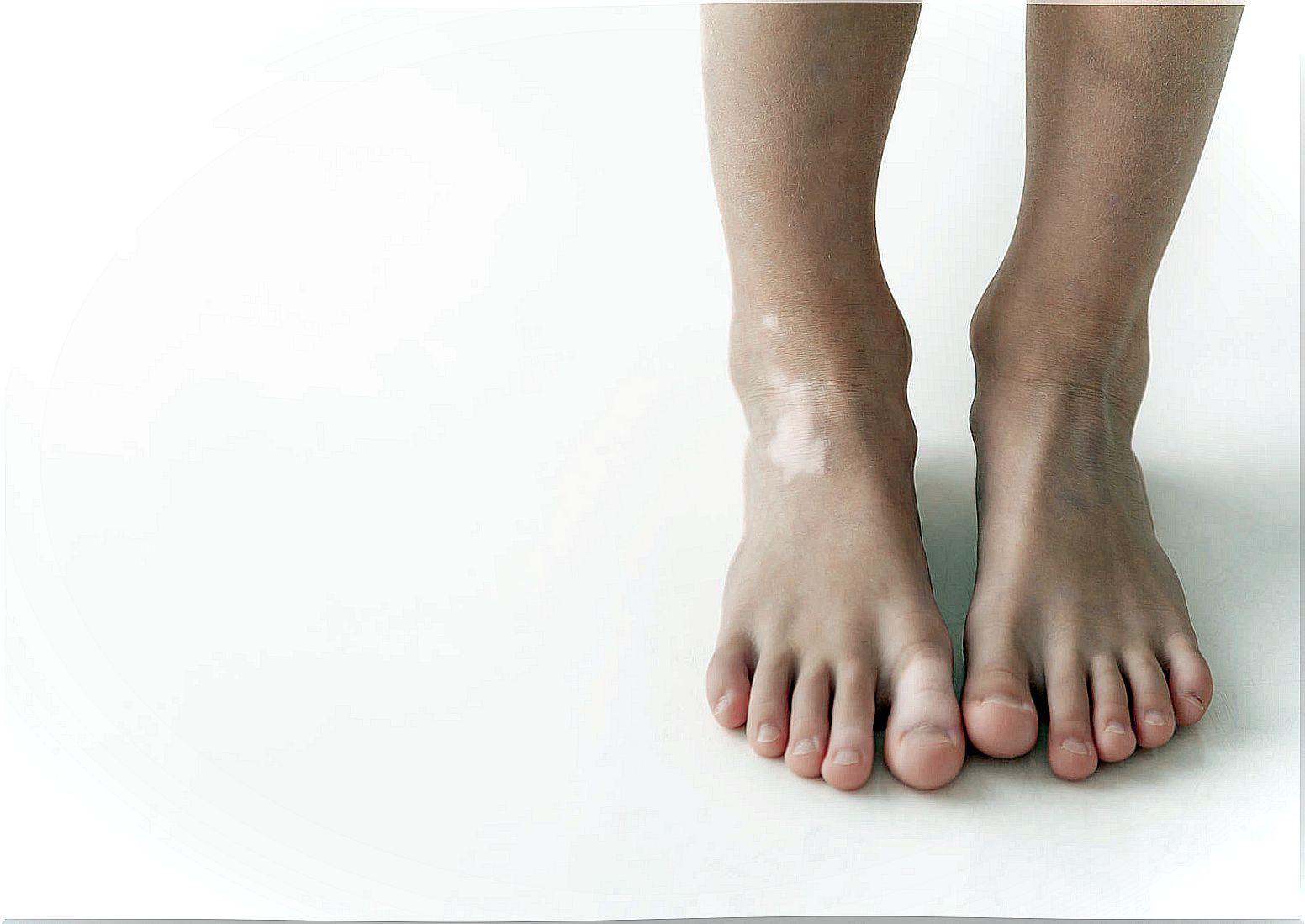
Pityriasis alba is one of the manifestations of the most common pigmentation disorders that can be seen in preadolescence. It is characterized by hypochromic spots on the face, preferably on the cheeks. In addition, it is a benign pathology that is not contagious and can resolve spontaneously over months or years.
Hypopigmented macules are more evident in dark phototypes and in the regions of the body most exposed to solar radiation.
Why is pityriasis alba generated?
Pityriasis alba is a disease that is observed throughout the world and does not present a genetic predisposition. However, there is a high prevalence in children of school age and from low social strata.
The affectation in children has a predilection for the areas of the face, while in adults it is spread throughout the body.
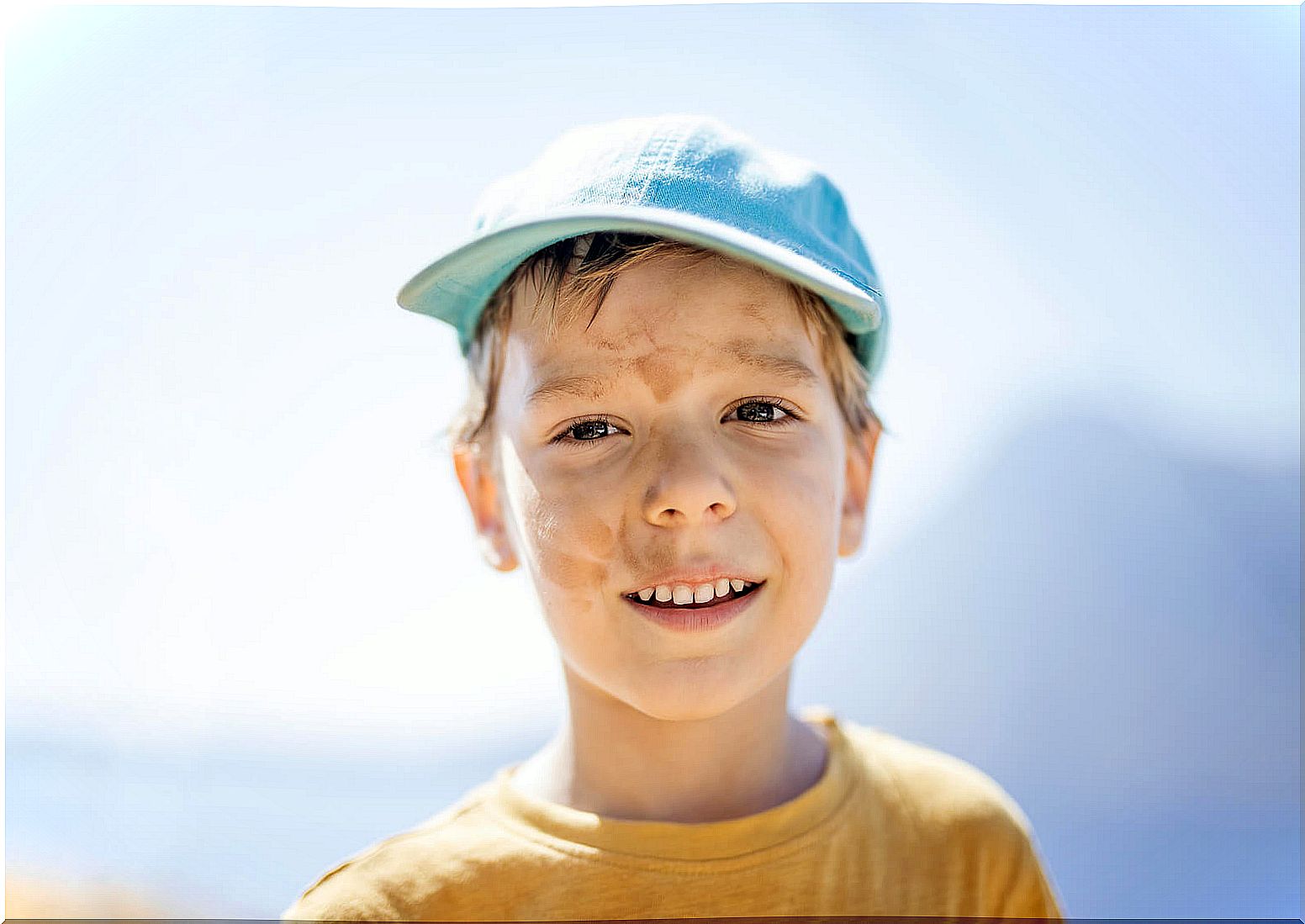

Its cause is still unknown, but some of the factors that could contribute to the presence of pityriasis alba, according to a publication by Cutis , are the following:
- Atopic dermatitis.
- Solar radiation.
- Xerosis.
- Vitamin deficiencies
Pityriasis alba is one of the minor criteria for diagnosing atopic dermatitis. Therefore, patients should be treated as atopic.
Symptoms of pityriasis alba
This type of pathology is usually not consulted because it goes unnoticed early, which generates an underreporting of the disease. Consequently, the clinical manifestations resolve spontaneously, without having received treatment and without being of any severity.
Pityriasis alba is characterized by the presence of oval or round patches with fine scaling, which do not present symptoms. In turn, their diameters range from 0.5 to 5 cm, with sharply undefined edges.
These lesions are usually asymptomatic but, on occasions, the patient may complain of pruritus (itching) in that area, as a Pediatric Dermatology review concludes .
They are located preferably on the face, but can also be seen on the back, trunk and upper extremities. Hypopigmented or pink spots, after being treated or having resolved spontaneously, do not leave sequelae. On the contrary, the skin recovers its tonality and the trace of a stain in that sector is imperceptible.
Clinical variants
There are variants in the clinical manifestations of this disease. Therefore, this polymorphism leads her to divide it into four different categories:
- Hypochromic : the most common variant .
- Erythematous : begins with pink spots.
- Follicular : around the hypochromic plaques, follicular hyperkeratosis can be observed.
- Pigmenting : the coloration of the lesions are bluish in the center, with loss of pigmentation in the perilesional region.
Differential diagnostics
The diagnosis is made at the time of medical consultation with the specialist through visual examination and correct questioning. In addition, no biopsy or mycological examination or the use of Wood’s lamp is required.
It should be taken into account that the manifestations of pityriasis alba are similar to other pathologies that involve the alteration of skin pigmentation. Some of these disorders are as follows:
- Pityriasis versicolor (of fungal origin).
- Vitiligo.
- Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation.
- Indeterminate leprosy.
- Mycosis fungoides.
What is the treatment for pityriasis alba?
Pityriasis alba is a disease that is not serious, however, it can affect the aesthetic appearance of those who suffer from it and alter the quality of life.
Daily moistening
The first line of treatment is moisturizing the skin, like all pathologies associated with atopic dermatitis. The ideal is to avoid that the skin is dry, so it is recommended not to use astringent soaps, extensive and hot showers or irritating products. In turn, moisturizing with emollients after each bath is a good care and prevention practice to avoid xerosis.
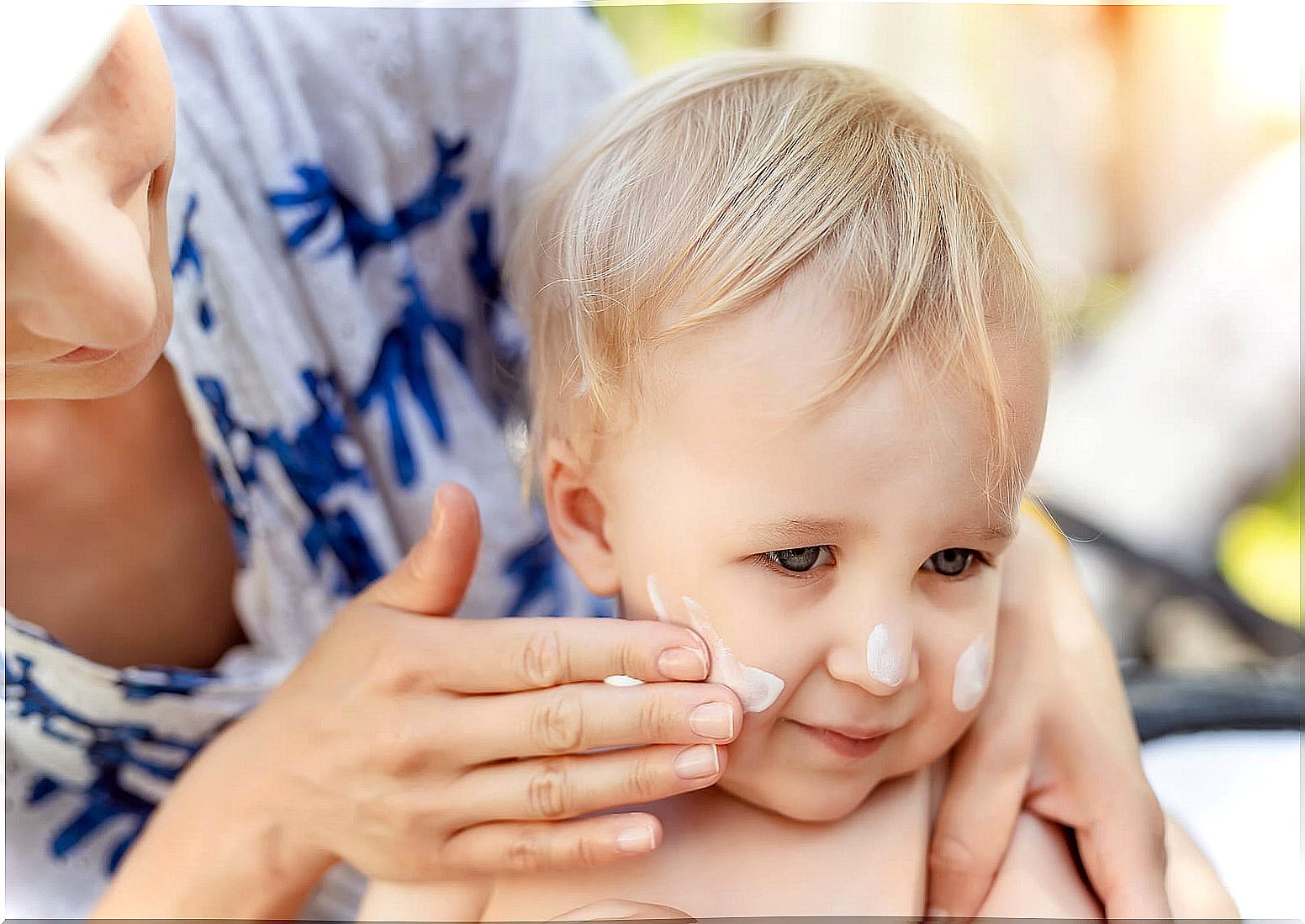

Solar protection
It is essential to apply suitable sunscreens, with their corresponding renewal every 2 hours, on the skin. Today, there are several presentations and colors of it that make it a more pleasant product to be used.
The sunscreen must have an SPF greater than or equal to 50 and the habit must be generated that, even if there are no visible sun rays, the skin needs to be protected in the same way. In addition, the use of physical barrier methods, such as hats, umbrellas, glasses and clothing with your own sunscreen is recommended.
Prescription creams
Low intensity corticosteroids are very useful in the inflammatory stages of the lesions. However, they should be used for very short periods of time to avoid later complications, such as skin atrophy, among others.
Another very effective therapeutic option is tacrolimus ointments, since they have the same efficacy as steroids, but without triggering unwanted adverse effects.
Now that you know more about this skin condition, do not hesitate to go to a healthcare professional if you notice any of the signs that we have just talked about and so that they can solve all the doubts that may arise.